Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


This prospective, observational study investigated the clinical outcomes of initiating triple-drug oral therapy in newly diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) presenting with glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) ≥9%.
Early initiation of glimepiride–metformin–pioglitazone therapy consistently delivers superior glycemic and lipid improvements with minimal hypoglycemic events in T2DM patients.
This prospective, observational study investigated the clinical outcomes of initiating triple-drug oral therapy in newly diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) presenting with glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) ≥9%.
Patients received a combination of three oral hypoglycemic agents during the first 3 months. Based on follow-up HbA1c values, therapy was subsequently tailored to dual-drug or single-drug regimens. All volunteers were monitored for 12 months. The evaluation focused on changes in HbA1c, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, body weight, waist circumference, dose adjustments, hypoglycemic events, patient-reported well-being, and overall treatment satisfaction.
A total of 137 volunteers completed the study. Over the study period, all key metabolic markers exhibited consistent and statistically significant improvement from baseline to 12 weeks, with further enhancement maintained through 52 weeks (Table 1).
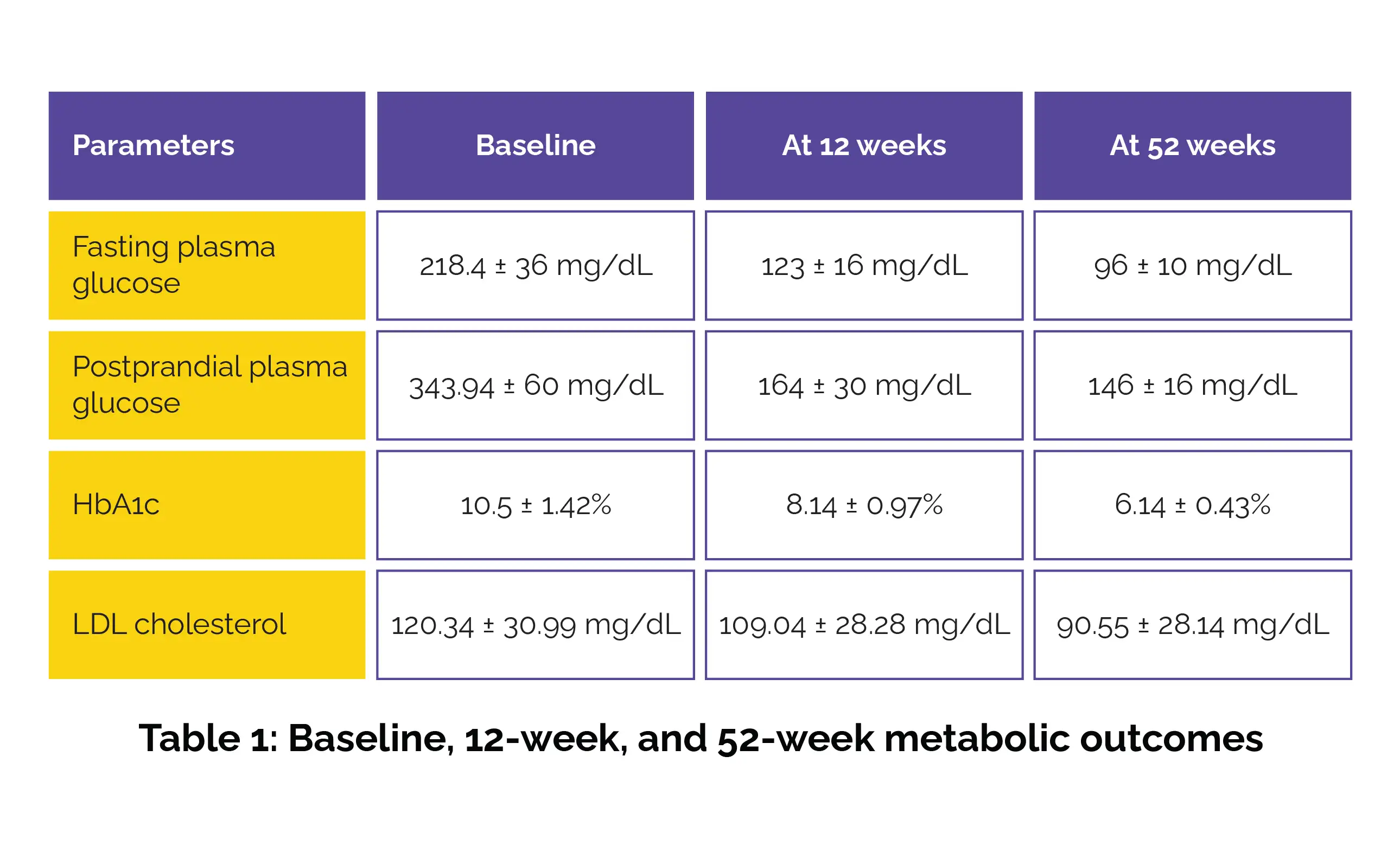
Early initiation of triple combination therapy using glimepiride, metformin, and pioglitazone demonstrates superior glycemic control, greater HbA1c reduction, and fewer hypoglycemic episodes compared to traditional stepwise add-on treatment. These findings support the use of early combination therapy to achieve faster and more sustained metabolic improvement in newly diagnosed T2DM patients.
Journal of Association of Physicians of India
Sustained Glycemic Control and Improved Well-being on Early Induction of Triple Drug Therapy in Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with HbA1c ≥9%: A Prospective, Cross-sectional, and Observational Study
Vivek Chauhan et al.
Comments (0)