Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


This study compared the therapeutic potential of mometasone furoate–azelastine hydrochloride nasal spray versus fluticasone furoate–azelastine hydrochloride nasal spray in allergic rhinitis (AR).
Both mometasone-azelastine and fluticasone-azelastine nasal sprays show comparable effectiveness in reducing allergic rhinitis symptoms. However, fluticasone-azelastine causes more bitterness and nasal irritation.
This study compared the therapeutic potential of mometasone furoate–azelastine hydrochloride nasal spray versus fluticasone furoate–azelastine hydrochloride nasal spray in allergic rhinitis (AR).
This multicenter, retrospective, comparative study was conducted across 30 ENT clinics. Patient medical records were assessed for demographics, clinical symptoms, treatment regimen, outcomes, and adverse events. Treatment efficiency was measured via the mean reduction in total nasal symptom score (TNSS) and non-nasal symptom scores from baseline to the end of intervention.
Overall, 235 patients received mometasone-azelastine and 221 received fluticasone furoate-azelastine intranasal spray. At day 14, no statistically significant difference was noted between the groups for mean reduction in TNSS, as depicted in Table 1:
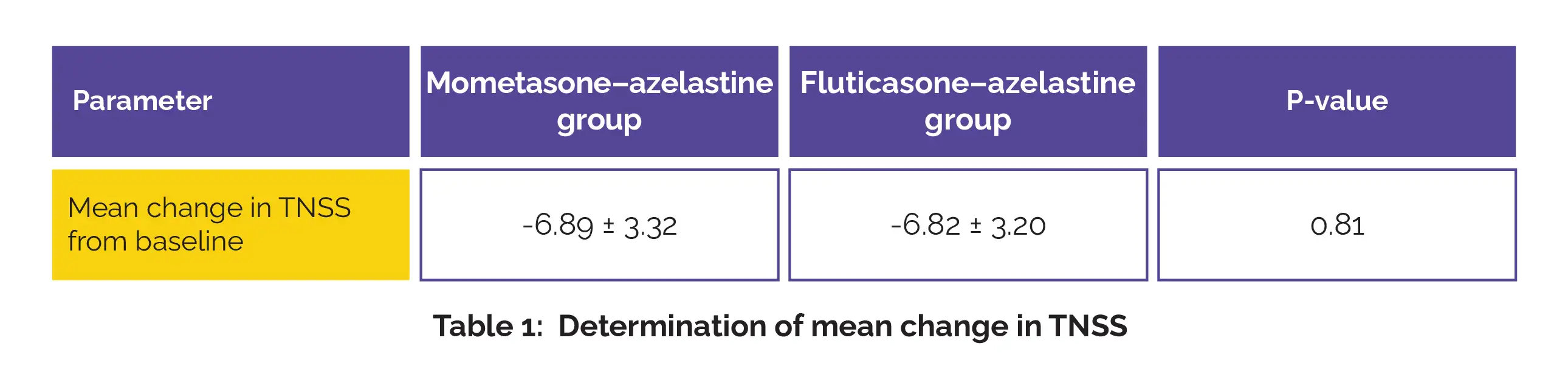
However, those treated with fluticasone-azelastine reported a significantly higher incidence of bitter taste and nasal discomfort. No treatment discontinuation, serious adverse events, or hospitalizations occurred in either group.
Both mometasone-azelastine and fluticasone-azelastine combination nasal sprays illustrated similar effectiveness in alleviating nasal and non-nasal AR symptoms by day 7 and day 14. However, the mometasone-based formulation exhibited better tolerability, with fewer reports of adverse taste and nasal irritation, making it a potentially preferable option for long-term management of AR.
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery
Comparative clinical assessment of mometasone furoate-azelastine hydrochloride intranasal spray (Ryaltris AZ®) with fluticasone furoate-azelastine hydrochloride intranasal spray in patients with allergic rhinitis in India
Kabikant Samantaray et al.
Comments (0)