Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


This trial compared the safety and efficacy of five main interventions used for H. pylori: triple-drug combination regimen, ciprofloxacin-based triple therapy, sequential therapy, hybrid (combined) therapy, and concomitant therapy.
Ciprofloxacin-based triple therapy achieves the highest eradication rate for H. pylori in the pediatric population, providing a more effective empirical treatment option compared to other regimens.
This trial compared the safety and efficacy of five main interventions used for H. pylori: triple-drug combination regimen, ciprofloxacin-based triple therapy, sequential therapy, hybrid (combined) therapy, and concomitant therapy.
A randomized controlled trial comprising 200 children (aged 3 to 16 years) with confirmed H. pylori infection was performed. They were allocated to one of the study interventions.
The success of the eradication was assessed through a stool antigen test performed four weeks after discontinuing antibiotics and two weeks following the cessation of proton pump inhibitors. The stool antigen assay was carried out using a monoclonal antibody kit based on the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method.
Epigastric pain was the most frequently reported symptom (79%). Gastric antral erythema was observed in 98% of cases, while antral nodularity was identified in 54.5% of cases during endoscopic examination. Histological evaluation showed infiltration of the superficial lamina propria by plasma cells and lymphocytes in all biopsies taken from the stomach mucosa.
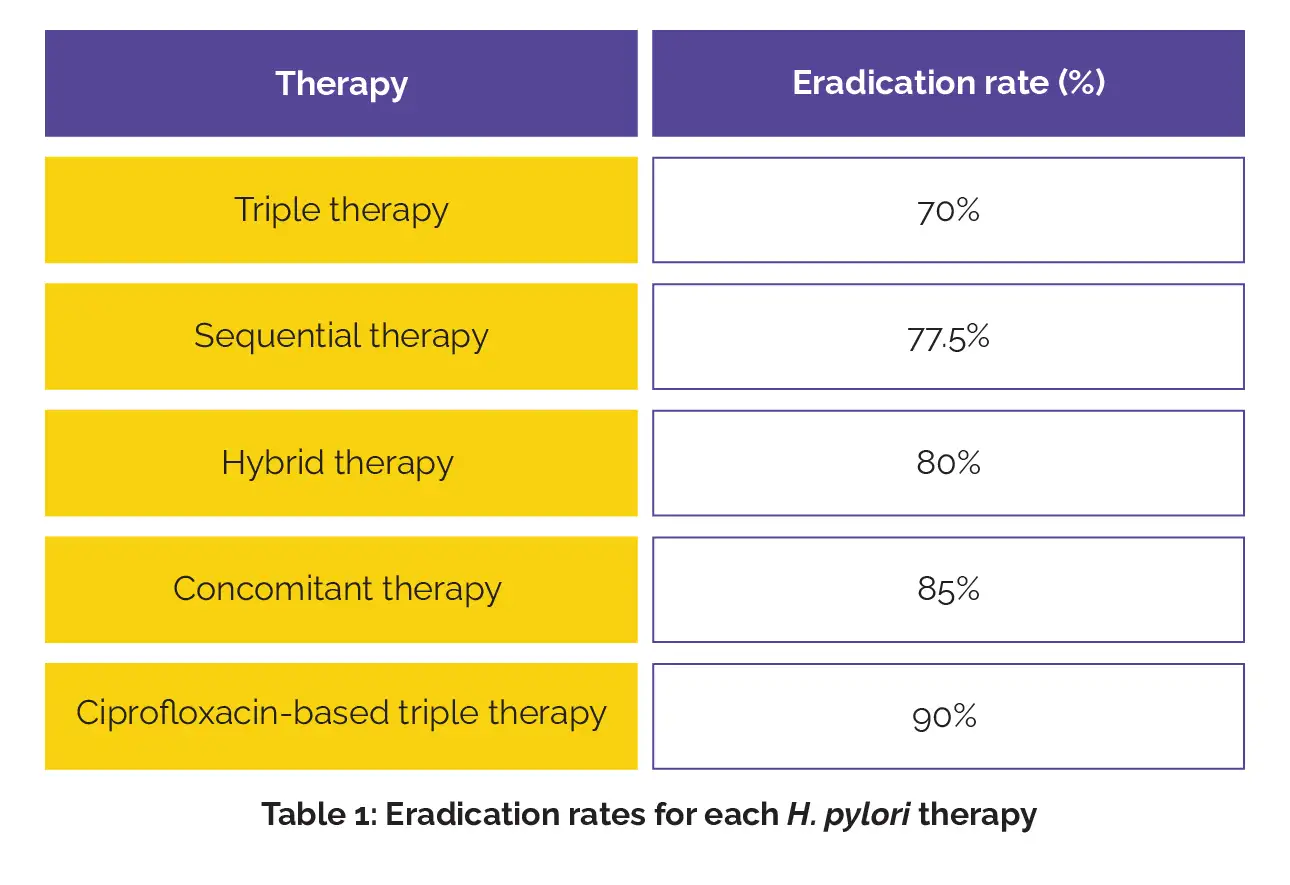
Active gastritis with neutrophilic infiltration was observed in 75% of cases, while gastric atrophy and intestinal metaplasia were relatively uncommon (8.5% and 1%, respectively). The eradication rates for the therapies under consideration have been mentioned in the following Table 1, with ciprofloxacin-based triple therapy displaying a significantly higher success rate compared to triple therapy (p = 0.025).
The incidence of adverse effects across different interventions did not show a statistically noteworthy difference.
Triple-drug regimen with ciprofloxacin showed the highest eradication rate and good tolerability, while other regimens offered no clear benefit over triple therapy for H. pylori infection in children.
European Journal of Pediatrics
Different regimens for eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection in children: a randomized controlled trial
Sana Hosny Barakat et al.
Comments (0)