Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Vaginal and combined oral–vaginal probiotic supplementation markedly lowers recurrence rates, prolongs the time to first symptomatic infection, and is well-tolerated in premenopausal women with recurrent UTIs.
As antibiotic resistance continues to rise globally, non-antibiotic strategies to prevent recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs) are urgently needed. A new study offers promising evidence that prophylactic probiotic supplementation can remarkably mitigate the risk of recurrent UTIs in premenopausal women.
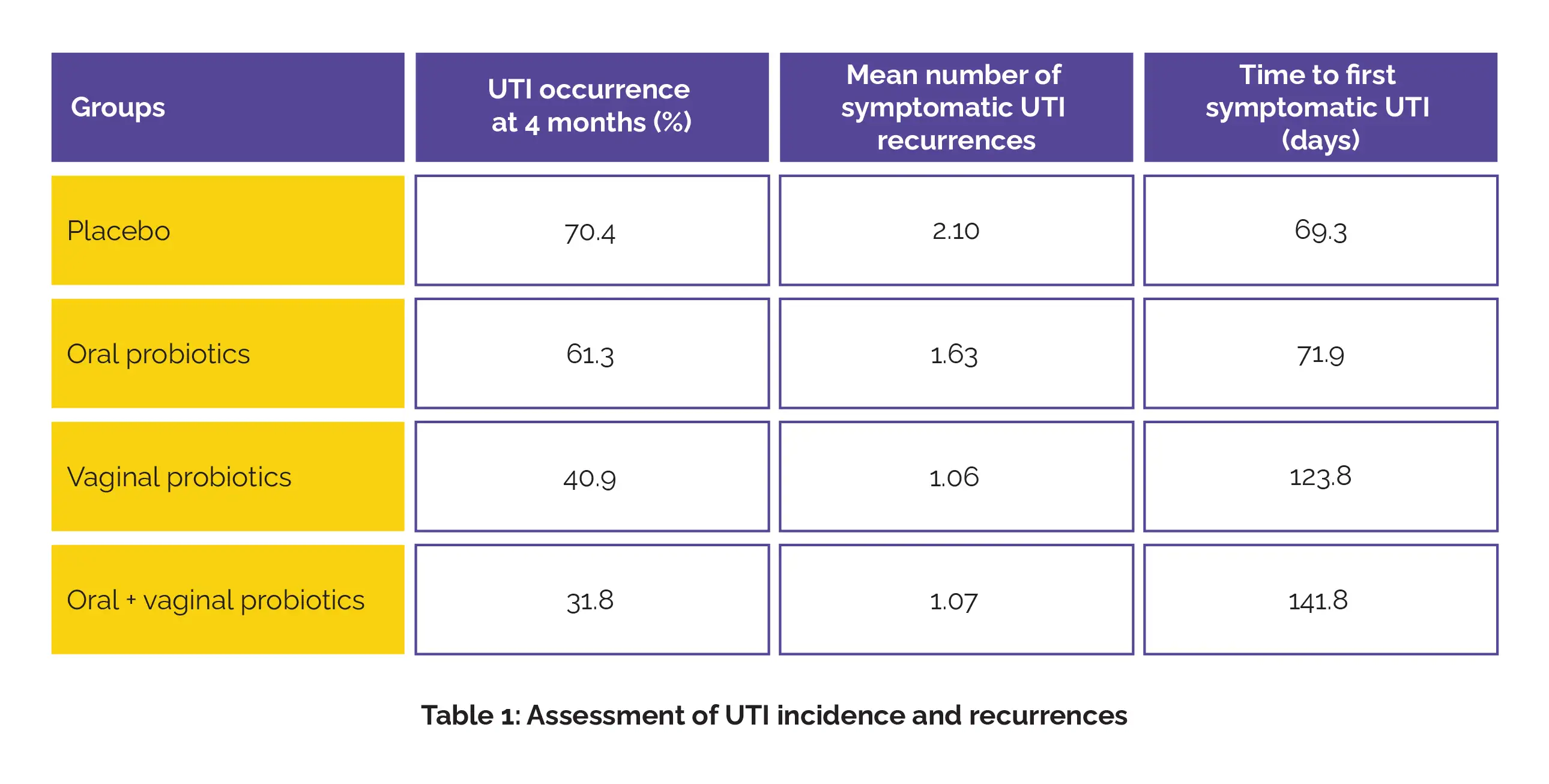
A total of 174 females with a past history of recurrent UTIs were randomly assigned to one of four groups for a 4-month intervention:
Participants were then monitored for symptomatic UTIs over a full year. The main outcomes ascertained were the total number of symptomatic UTIs over 4 months, the percentage of women experiencing at least one symptomatic UTI, and the duration until the first symptomatic UTI occurred. The findings were striking!
After 4 months, UTI incidence was highest in the placebo and oral-only groups, while participants receiving vaginal probiotics or the combined oral and vaginal regimen experienced notably fewer infections. Similarly, the number of symptomatic UTI recurrences was considerably lower, and the time to the first symptomatic UTI was considerably longer, in the vaginal and combination groups compared with the placebo and oral-only groups (Table 1).
Importantly, the probiotics were well-tolerated, with no serious side effects reported, making them a safe preventive option. These results suggest that vaginal probiotics—either alone or combined with oral supplementation—could yield a practical, non-antibiotic strategy for women prone to recurrent UTIs, potentially reducing reliance on antibiotics and helping combat the growing threat of antimicrobial resistance.
Clinical Infectious Diseases
Effectiveness of Prophylactic Oral and/or Vaginal Probiotic Supplementation in the Prevention of Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial
Varsha Gupta et al.
Comments (0)