Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


GLP-1 receptor agonists and phentermine-topiramate are the most potent drugs for reducing body weight in people with overweight or obesity. Among GLP-1 agents, semaglutide appears to deliver the greatest overall benefit.
A systematic review and network meta-analysis has revealed that modern weight-loss medications—particularly semaglutide, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and phentermine-topiramate—deliver substantially greater weight reduction when compared to lifestyle modification alone.
Obesity is a global public health crisis, and while lifestyle intervention remains the first-line therapy, many adults require additional support. Pharmacotherapy has emerged as an alternative, but until now, comparative evidence between weight-loss drugs has been limited. Published in "The Lancet", this study represents one of the most comprehensive evaluations conducted to date.
Investigators analyzed 132 randomized controlled trials, enrolling 48,209 adults with overweight or obesity. Databases searched included Embase, PubMed, and the Cochrane Library (CENTRAL). All medications evaluated were more effective than lifestyle changes alone. However, the extent of benefit varied substantially. Among all medications reviewed, semaglutide showed the greatest weight-loss effect, making it one of the most promising obesity treatments currently available. (Table 1).
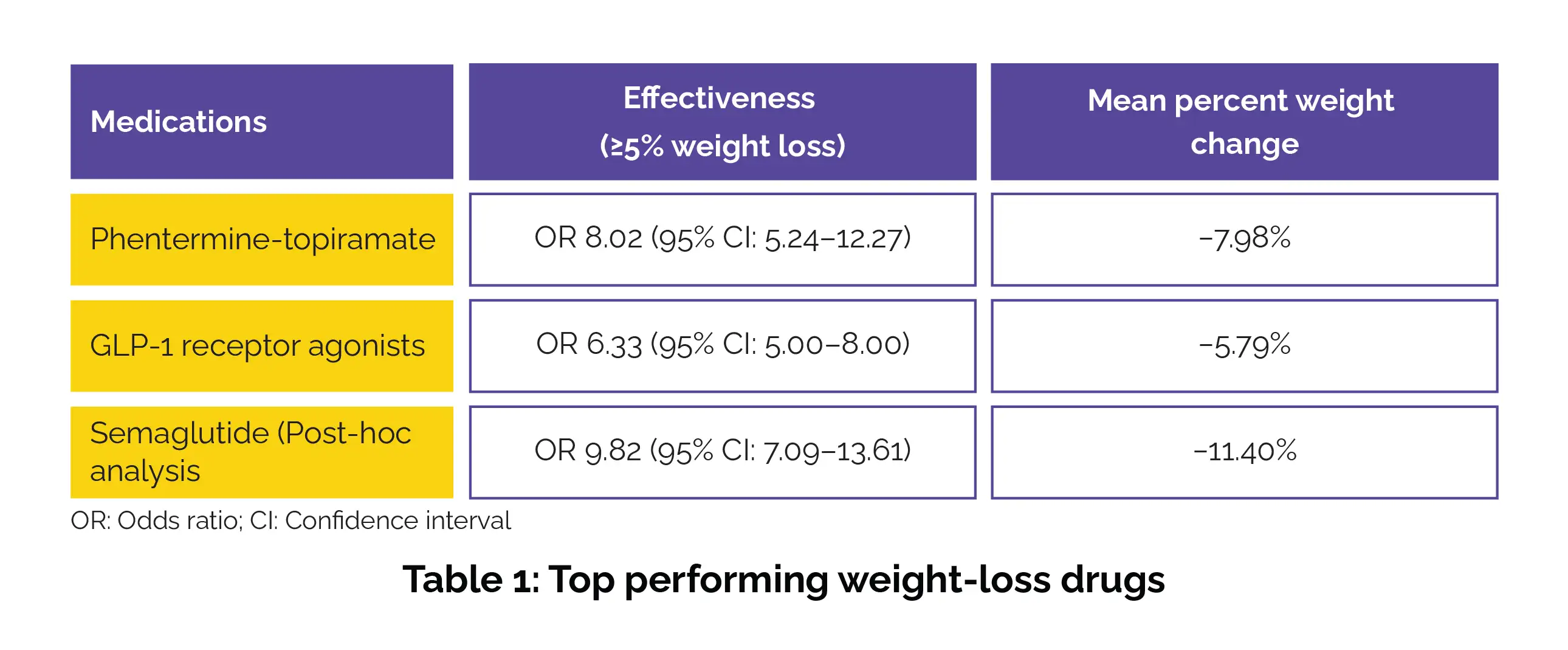
However, semaglutide produced substantial weight reduction without significantly higher dropout rates compared to other medications, suggesting a favorable benefit-risk balance.
The Lancet
Pharmacotherapy for adults with overweight and obesity: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials
Qingyang Shi et al.
Comments (0)