Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Acupuncture combined with targeted therapies effectively reduces pain, improves disability and quality of life, enhances neurological recovery, and lowers inflammation in lumbar disc herniation–related sciatica.
A recent network meta-analysis has revealed that acupuncture, particularly when combined with other therapies, offers superior results compared to conventional rehabilitation methods.
Sciatica resulting from lumbar disc herniation (LDH) is a disabling ailment with substantial personal and socioeconomic impact. While acupuncture is increasingly used worldwide as a non-pharmacological therapy, clinicians still lack clarity on which acupuncture methods yield the strongest therapeutic advantage.
To address this gap, Dongyi Ni et al. compared the effectiveness and safety of multiple acupuncture techniques, including monotherapies, acupuncture-based combinations, and acupuncture versus conventional rehabilitation. A comprehensive search was executed across 8 databases, including PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and major Chinese medical repositories.
Key methodological steps included:
This framework allowed precise cross-comparisons between direct and indirect evidence to determine the most effective interventions. The analysis demonstrated clear superiority of combination acupuncture therapies (Table 1):
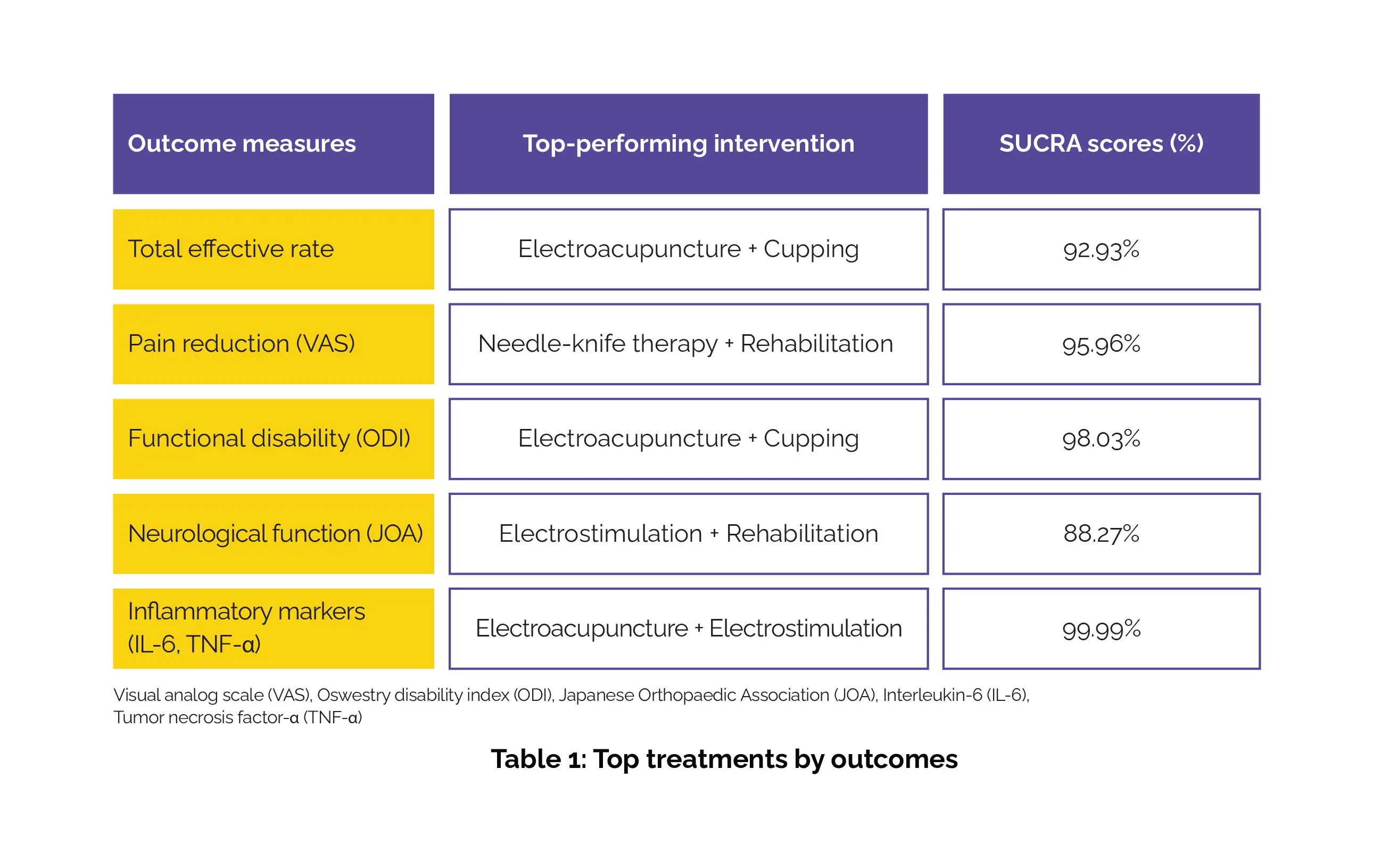
Multimodal acupuncture-based combinations consistently outperformed monotherapies and standard rehabilitation, delivering superior improvements across pain, disability, neural recovery, and inflammation. The study concluded that acupuncture-combined therapies offered the strongest therapeutic benefits for sciatica secondary to LDH. The interventions significantly improved pain, functional disability, neurological function, and inflammatory status, surpassing both rehabilitation alone and acupuncture monotherapy. These findings highlight integrated acupuncture strategies as high-value, non-invasive treatment options for LDH-related sciatica.
Journal of Pain Research
Efficacy and Safety of Acupuncture and Acupuncture-Combined Therapies in the Treatment of Sciatica Caused by Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Network Meta-Analysis
Dongyi Ni et al.
Comments (0)