Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Using a topical probiotic nano-formulation from Lactobacillus reuteri three times daily reduces lesion size and pain severity in recurrent aphthous stomatitis patients faster than a local analgesic oral rinse.
In a randomized controlled trial published in "BMC Oral Health", researchers have unveiled a novel approach to tackling recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS), a painful condition affecting millions worldwide. According to the findings, a probiotic nano-formulation derived from Lactobacillus reuteri shows potential as a promising therapeutic approach for RAS (a common type of oral ulcer). The study, conducted by a team of experts, assessed the effects of a topical probiotic nano-formulation procured from Lactobacillus reuteri.
A total of 60 participants were enrolled in the trial, with individuals allocated into two groups: the probiotic group and the control group. The probiotic group received the topical probiotic nano-formulation thrice a day for about 7 days, while the control group was given a standard analgesic oral rinse. Throughout the intervention period, the size of ulcers and intensity of pain were meticulously documented on days 0, 3, 5, and 7.
Prior to the intervention, both groups illustrated no vital differences in lesion size and intensity of pain. Remarkably, participants in both groups experienced profound reductions in pain intensity and lesion size over the course of the study. However, after just one week, the probiotic group demonstrated notably larger reductions in lesion size compared to the control group, with a profound difference (P-value = 0.01), as shown in Figure 1:
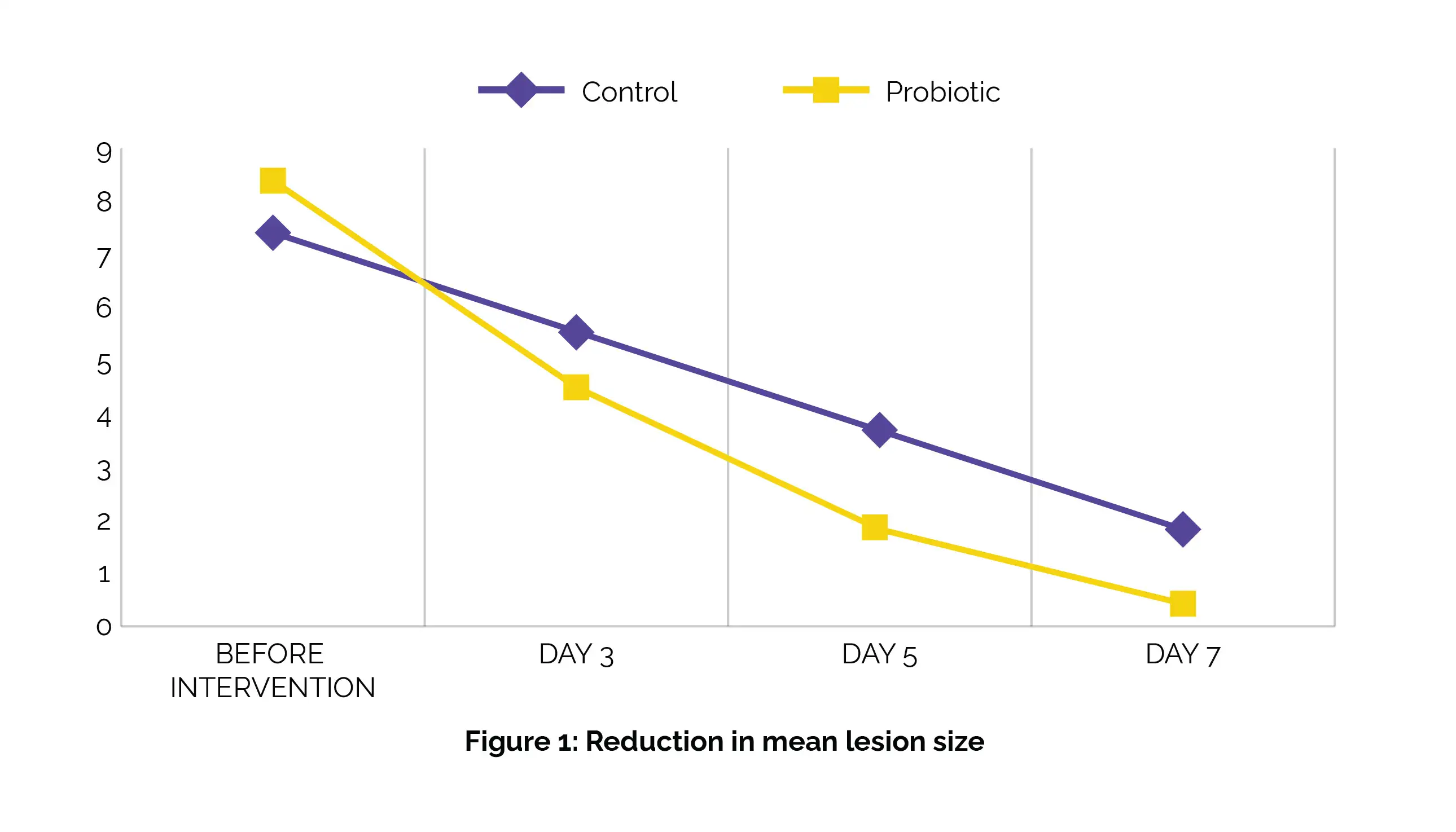
Additionally, the probiotic group illustrated a significantly greater decrease in pain severity when compared to the control group (P-value = 0.04), as shown in Figure 2:
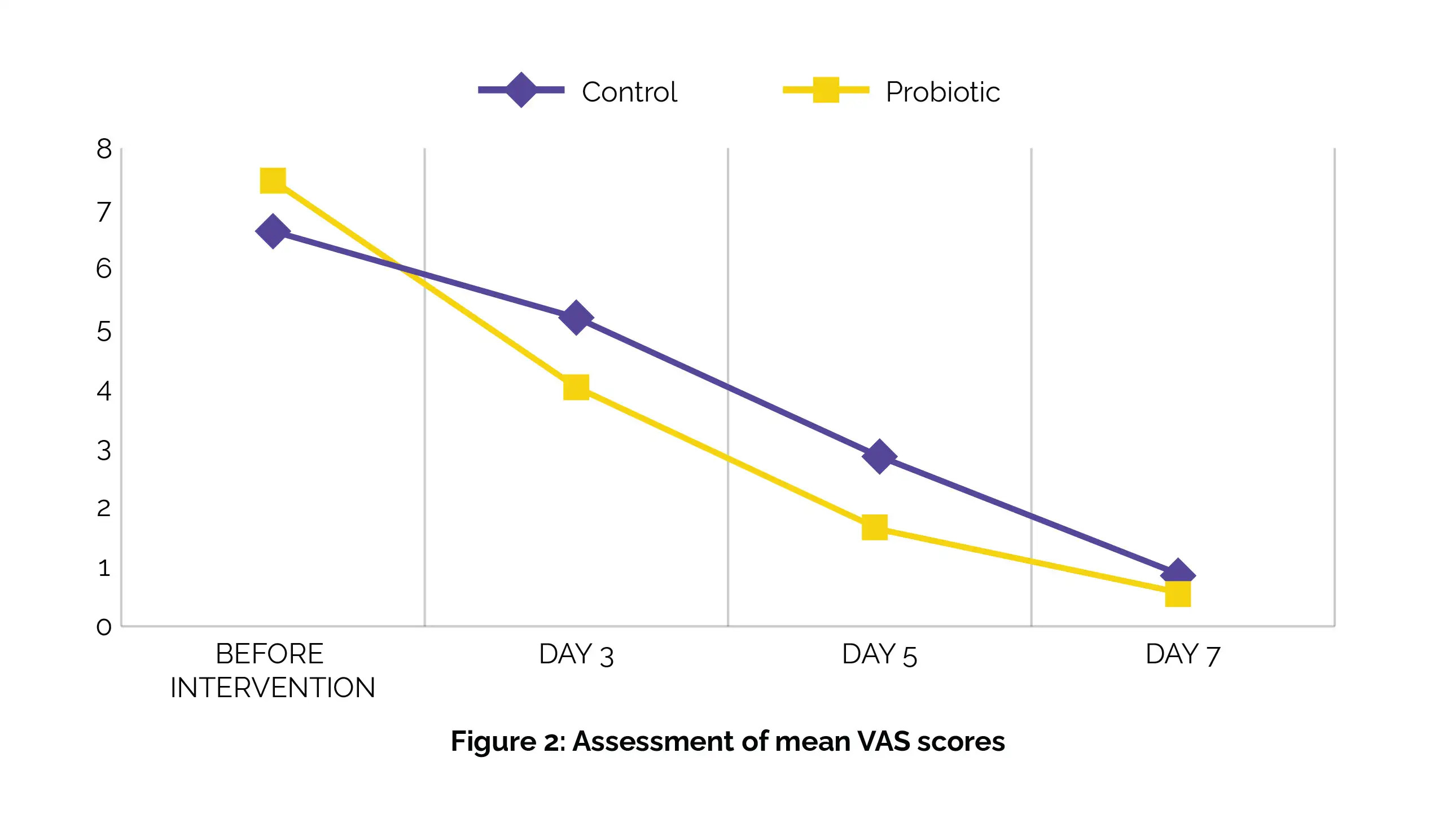
These findings underscore the potential of applying topical probiotic nano-formulation derived from Lactobacillus reuteri as a promising choice for RAS. The rapid decrease in lesion size and pain severity observed in the probiotic group highlights the efficacy of this innovative approach compared to traditional analgesic oral rinses. Hence, Lactobacillus reuteri-derived probiotic nano-formulation could revolutionize RAS management, providing patients with a faster and more efficient means of alleviating symptoms and improving quality of life.
BMC Oral Health
Effect of lactobacillus reuteri-derived probiotic nano-formulation on recurrent aphthous stomatitis: a double-blinded randomized clinical trial
Nazafarin Samiraninezhad et al.
Comments (0)