Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Achieving symptom-free periods is the top priority for chronic spontaneous urticaria patients, even if it means accepting trade-offs such as the mode of administration.
A new cross-sectional study, CHOICE-CSU, offered valuable insights into what patients prioritize in injectable treatments for chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU), particularly those inadequately controlled by H1-antihistamines.
This patient preference study followed a two-phase approach to understand what matters most to CSU patients when choosing injectable biologic products. The first phase gathered patient insights on key treatment attributes, such as efficacy, safety, and administration mode, which were then used to design realistic treatment profiles. In the second phase, patients participated in a discrete choice experiment (DCE), selecting between 12 hypothetical treatment pairs.
Using hierarchical Bayesian logistic regression, researchers quantified the relative importance of each attribute, revealing the trade-offs patients are willing to make in their treatment decisions. In total, 450 respondents took part in the DCE. Table 1 summarizes the most influential attributes:
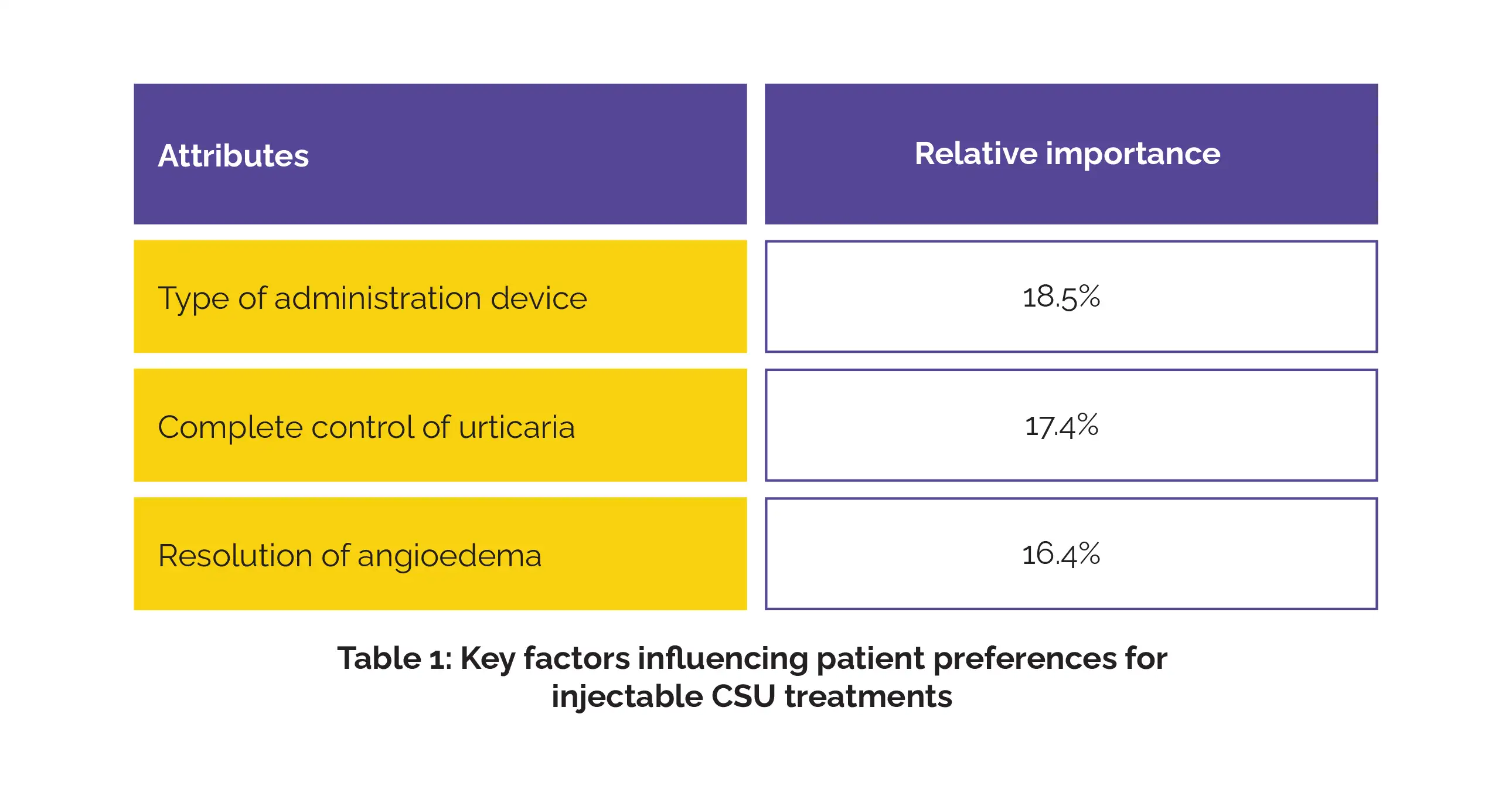
Notably, when efficacy was equal, most patients (72.9%) chose auto-injectors over pre-filled syringes (27.1%), highlighting a strong inclination for convenience in treatment administration.
While symptom-free periods remained the primary treatment goal, patients were willing to compromise on convenience for better efficacy. As new oral therapies become available, further research is needed to explore patient inclination for oral vs. injectable treatments.
The Patient
Assessing Preferences of Patients with Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria for Injectable Treatment Profiles
Ana Maria Giménez-Arnau et al.
Comments (0)