Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Bempedoic acid (180 mg/day) markedly reduces LDL-C levels and improves overall lipid profiles in hypercholesterolemia patients who are unable to reach target lipid levels with statins alone or who are statin-intolerant.
A recent phase 3 clinical trial conducted in Japan, known as the CLEAR-J study, has illustrated that bempedoic acid is an effective, safe, and well-tolerated oral therapy for lowering low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in hypercholesterolemia patients who either have an inadequate response to statins or are intolerant to them.
Statins are the standard intervention for lowering LDL-C, but many individuals are unable to achieve target cholesterol levels or discontinue treatment due to deleterious effects such as muscle pain. Bempedoic acid, a small-molecule drug that suppresses ATP citrate lyase—an enzyme involved earlier in the cholesterol synthesis pathway than statins—offers a promising alternative for this population. Hence, this study sought to investigate bempedoic acid's efficacy and safety for hypercholesterolemia.
Japanese patients with poorly controlled LDL-C despite statin use or who were statin-intolerant were randomized to get either bempedoic acid 180 mg/day or placebo for 12 weeks. The percentage alteration in LDL-C levels from baseline to week 12 was the key outcome ascertained. Results showed a substantial LDL-C reduction in the bempedoic acid group as opposed to the placebo group. Secondary endpoints also favored bempedoic acid in terms of non-high-density lipoprotein (non-HDL) cholesterol levels, total cholesterol levels, apolipoprotein B, as shown in Table 1:
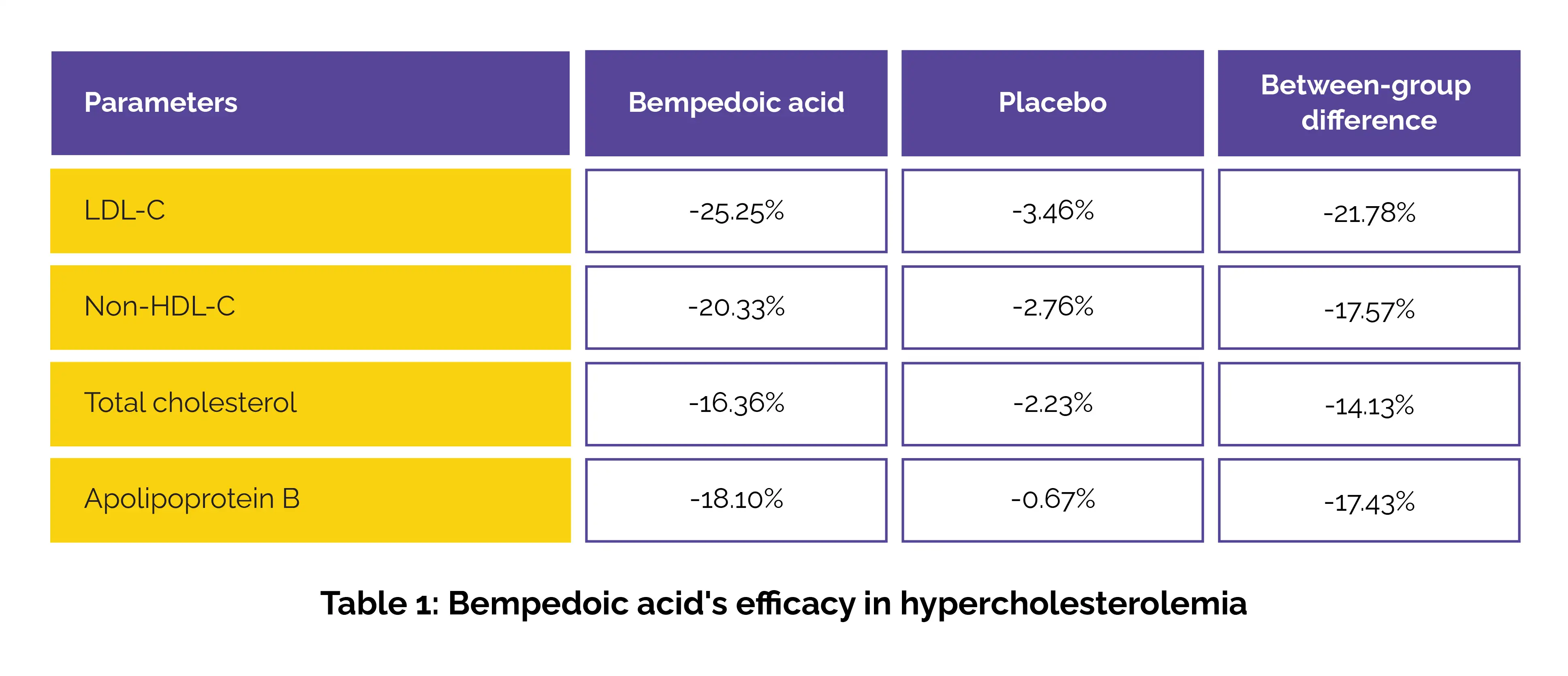
Notably, 62.5% of patients receiving bempedoic acid achieved their target LDL-C levels by Week 12. The treatment showed good tolerability, with treatment-emergent adverse events reported in 3 subjects in the bempedoic acid arm and 2 in the placebo arm. No novel safety concerns were identified. With its distinct mechanism of action and oral formulation, bempedoic acid may serve as a valuable addition to lipid-lowering strategies in clinical practice.
Circulation Journal
Efficacy and Safety of Bempedoic Acid in Japanese Patients With Hypercholesterolemia - A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 3 Study (the CLEAR-J Trial)
Shizuya Yamashita et al.
Comments (0)