Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


This retrospective cohort study explored the potency of liraglutide and semaglutide in decreasing body weight.
Both liraglutide and semaglutide show similar weight loss benefits. However, semaglutide achieves superior HbA1c reduction.
This retrospective cohort study explored the potency of liraglutide and semaglutide in decreasing body weight.
In this study, adult patients who received either liraglutide or semaglutide were included. The primary outcome was weight reduction, while the secondary outcomes encompassed changes in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and lipid profile.
A total of 366 patients were analyzed, with 122 receiving liraglutide and 244 receiving semaglutide. Baseline traits were similar between the groups, including mean age and mean body weight. The median follow-up was longer in the liraglutide arm as opposed to the semaglutide arm. At follow-up, both groups attained comparable median weight change and reduction in mean body weight. However, HbA1c reduction was more pronounced with semaglutide than with liraglutide, as shown in Table 1:
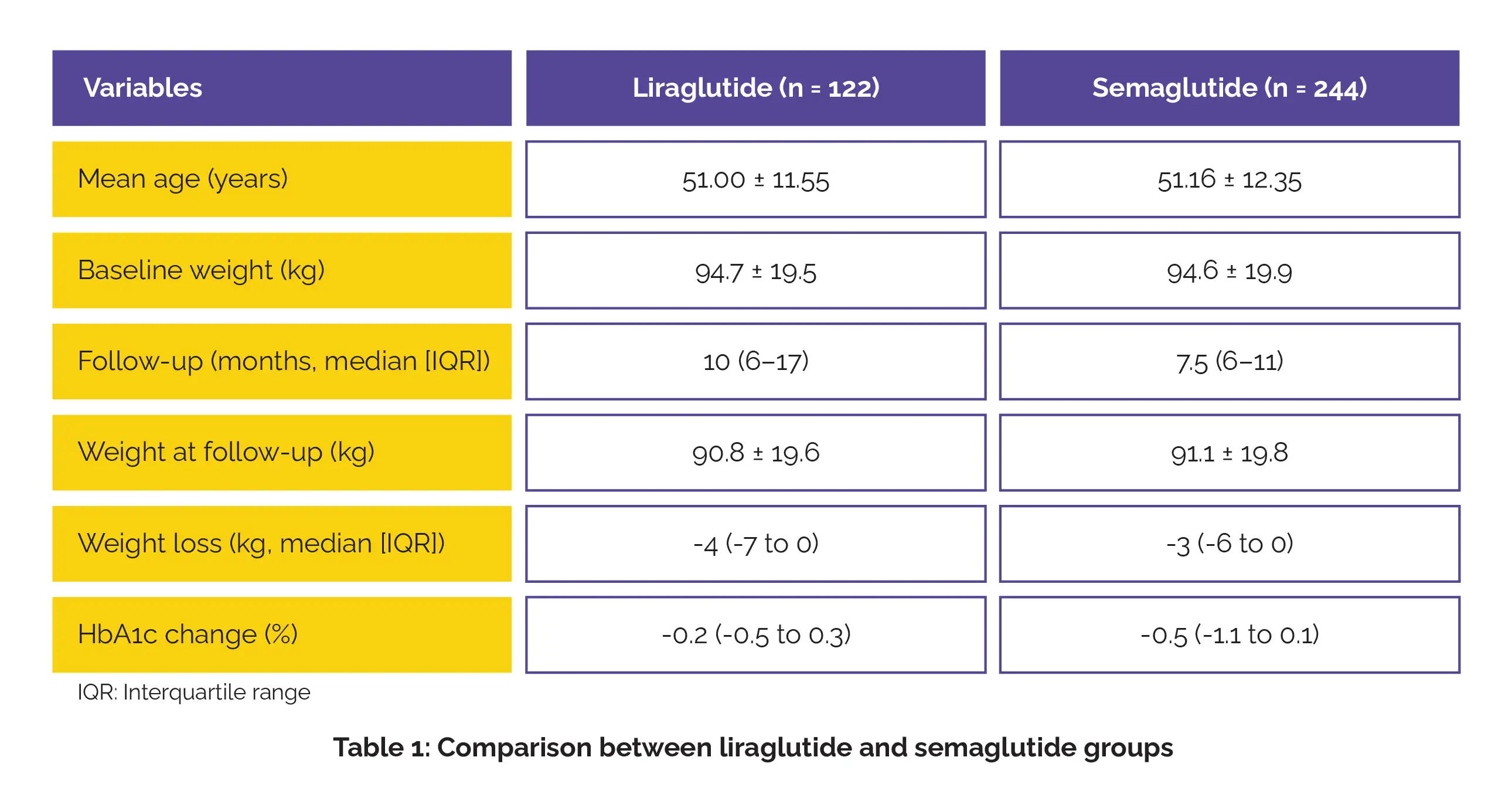
Both drugs markedly lowered triglycerides and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol. Regression analysis indicated no pivotal difference in weight loss between drugs (B -0.577), although baseline weight, diabetes, and sodium-glucose transport protein 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor use were independent predictors of weight change.
Both liraglutide and semaglutide achieved meaningful weight reduction, with no vital difference between the two. Semaglutide, however, offered greater improvement in the levels of HbA1c.
Hospital Pharmacy
Comparing the Efficacy of Liraglutide and Semaglutide on Weight Loss: Experience from the Middle East Gulf Region and Literature Review
Wasim S El Nekidy et al.
Comments (0)