Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Type 2 diabetes (T2D), a chronic condition caused by insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction, leads to high blood sugar, which is often considered difficult to control with lifestyle changes and oral medications.
Lobeglitazone added to metformin and sitagliptin provides a powerful triple therapy that lowers HbA1c by 1%, improves insulin sensitivity, and enhances lipid profiles, offering a safe and effective option for patients with uncontrolled blood sugar.
Type 2 diabetes (T2D), a chronic condition caused by insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction, leads to high blood sugar, which is often considered difficult to control with lifestyle changes and oral medications. Early and effective combination therapy is fundamental for preventing complications and boosting treatment outcomes. Metformin continues to be the standard first-line therapy for T2D because of its proven effectiveness and affordability.
Sitagliptin, the earliest dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor, has the strongest supporting evidence within its drug class. Compared to Western populations, Asians typically exhibit greater insulin secretion defects owing to reduced beta-cell mass and function, which makes them more responsive to DPP-4 inhibitors. For this reason, metformin combined with a DPP-4 inhibitor is the most common strategy in Korean patients. However, as dual therapy often has limited durability and diabetes tends to progress over time, the use of triple oral therapy is becoming increasingly common.
Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) improve insulin sensitivity, but older drugs in this class have safety concerns. Lobeglitazone, a new TZD, shows stronger effects and better safety in preclinical and clinical studies. It helps improve insulin secretion, reduces cellular stress, and exhibits anti-inflammatory properties, all of which contribute to protecting β-cell function and enhancing blood sugar control. Early clinical trials suggest lobeglitazone is safe, with fewer serious side effects compared to other TZDs.
Because of these benefits, lobeglitazone could be a useful third drug added to metformin and sitagliptin, especially in Asian patients who often include older and non-obese individuals. While SGLT-2 inhibitors are preferred for triple therapy in some guidelines, TZDs like lobeglitazone may offer a good alternative. However, there is limited research on adding a TZD to dual therapy with metformin and DPP-4 inhibitors.
Objective
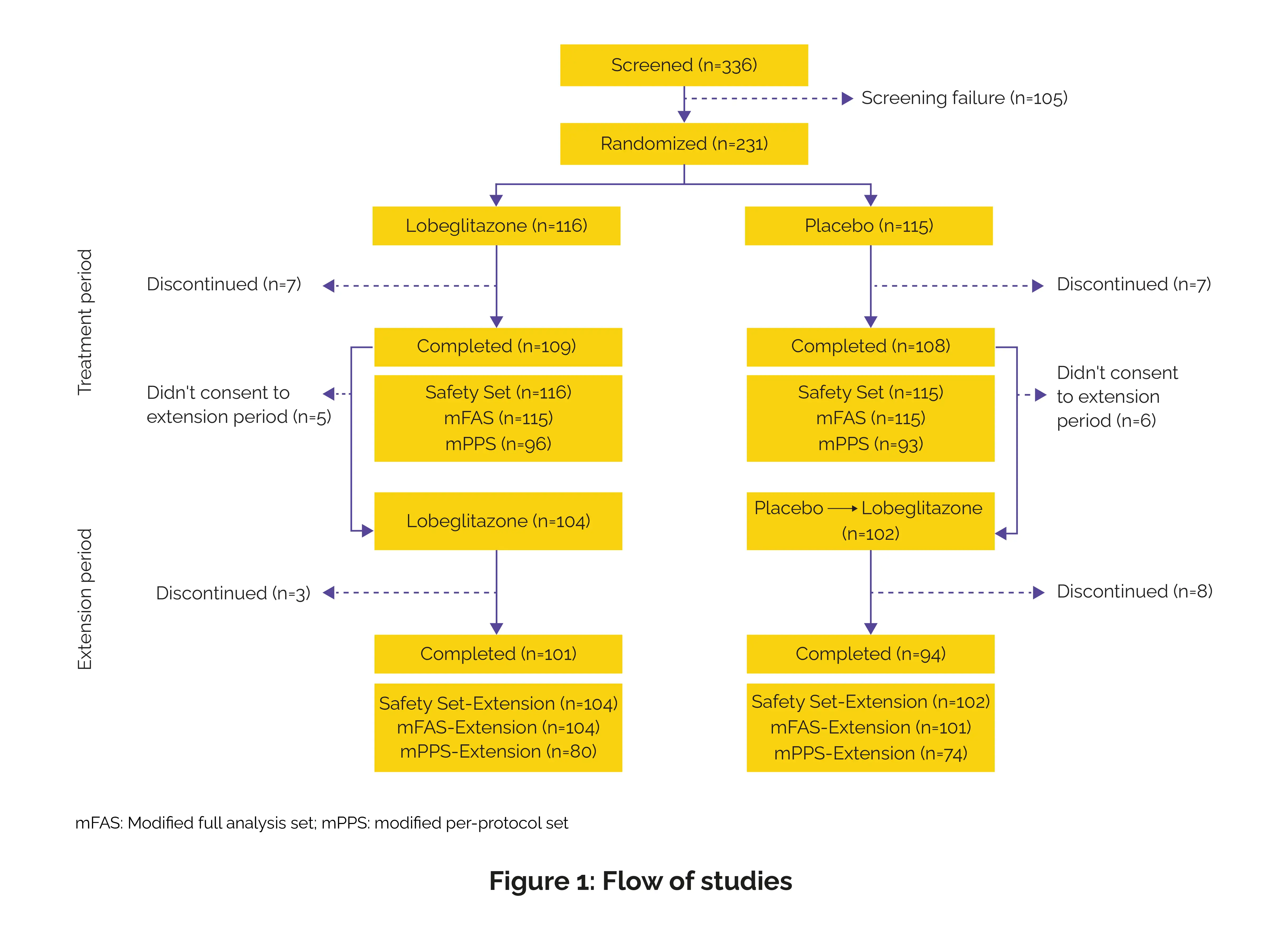
This randomized, placebo-controlled, phase III clinical trial evaluated the efficiency and safety of lobeglitazone as an add-on therapy to metformin and sitagliptin in Korean patients with T2D who had inadequate glycemic control with dual oral therapy.
This 52-week trial was conducted across 19 clinical sites in the Republic of Korea between April 2018 and December 2021 in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines, and the International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) standards.
Inclusion criteria
Participants were included if they:
Exclusion criteria
Data extraction
Study outcomes
(a) Primary endpoint
(b) Secondary endpoints
(c) Safety outcomes
Data and statistical analysis
Key findings
This study highlights lobeglitazone’s strong efficacy as an add-on therapy, achieving a remarkable 1% reduction in HbA1c at 24 weeks, which exceeds typical reductions seen with other triple therapy combinations. The glycemic benefits persisted through 52 weeks, alongside notable improvements in insulin resistance and β-cell function, even in patients with long-standing diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin and DPP-4 inhibitors.
The sustained reduction highlights the glucose-lowering potency of lobeglitazone and reinforces the durability of TZD therapy that has been demonstrated in previous studies, including real-world data showing efficiency for up to 42 months in over 2,000 patients. Lobeglitazone demonstrated a favorable safety profile, with only mild oedema and manageable weight gain observed.
Additionally, it positively influenced lipid metabolism by reducing small dense LDL-C and free fatty acids while increasing HDL-C, suggesting potential cardiovascular benefits. While results are promising, longer-term studies are warranted to confirm sustained effectiveness and safety. Overall, lobeglitazone appears to be a valuable addition to triple therapy regimens, offering enhanced glycemic control and metabolic improvements that may contribute to better long-term outcomes in T2D management.
Lobeglitazone added to metformin and sitagliptin combination therapy showed consistent glycemic efficacy, enhanced insulin dynamics, and favorably modified lipid parameters, presenting a well-tolerated and effective option for patients with inadequately controlled T2D.
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
Efficacy and safety of lobeglitazone added to metformin and sitagliptin combination therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes: A 52-week, multicentre, randomized, placebo-controlled, phase III clinical trial
Eun-Gyoung Hong et al.
Comments (0)