Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Adding vitamin D to UDCA therapy strengthens liver function, reduces fibrosis, and improves treatment response in primary biliary cholangitis patients.
A randomized controlled trial conducted by Yilihamu Abulitifu et al. assessed the impact of vitamin D (Vit D) supplementation alongside ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) on therapeutic response and liver fibrosis in primary biliary cholangitis (PBC). Conducted between May 2021 and December 2022, this prospective study analyzed 60 treatment-naive PBC patients. All the participants received UDCA capsules orally for 1 year and were randomly divided into 2 groups:
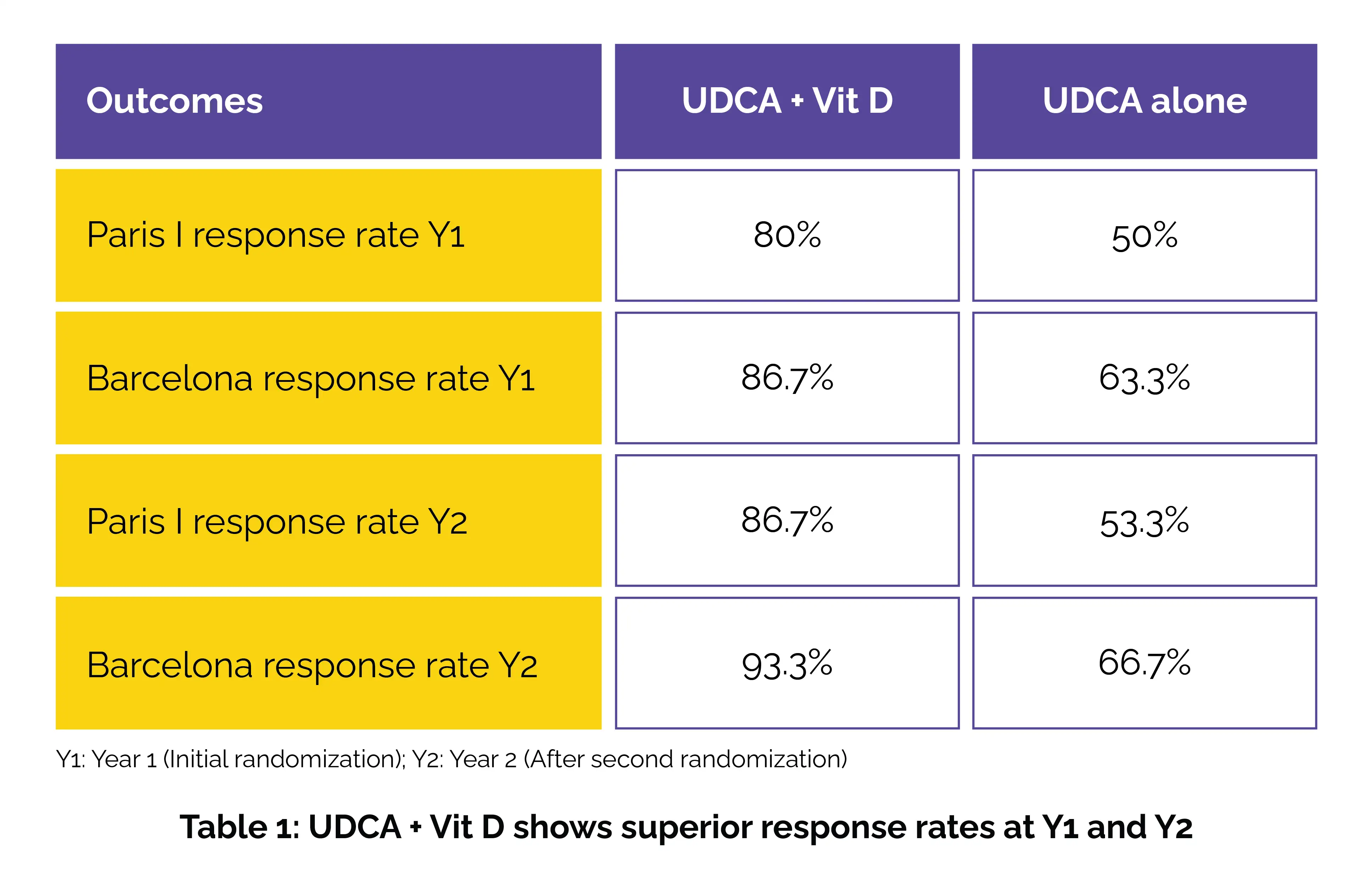
Following 1 year of treatment, the UDCA-only group was further segregated and treated for an additional year, allowing researchers to reassess the role of Vit D when added to UDCA therapy. Clinical symptoms, laboratory tests, and imaging data were collected pre and post-intervention. Potency was evaluated via the Paris I and Barcelona criteria, and liver stiffness measurement (LSM) was estimated via FibroTouch.
After 1 year, those receiving UDCA + Vit D illustrated significant biochemical and clinical improvements compared to those on UDCA alone:
The combination of UDCA and vitamin D produced higher treatment response rates than UDCA alone under both the Paris I and Barcelona criteria. This superiority was maintained during the second year of the study, with the UDCA + Vit D subgroup continuing to show better outcomes than the UDCA monotherapy subgroup (Table 1).
This study yields compelling evidence that vitamin D supplementation enhances the therapeutic effect of UDCA in primary biliary cholangitis. The combination not only improves liver function and biochemical indices but also minimizes hepatic fibrosis, potentially raising long-term treatment success.
BMC Gastroenterology
The effectiveness of combining ursodeoxycholic acid with vitamin D in treating patients with primary biliary cholangitis and its impact on hepatic fibrosis: a randomized trial
Yilihamu Abulitifuet et al.
Comments (0)