Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Both intranasal dexmedetomidine (2.5 μg/kg) and oral lorazepam (2 mg) improve sleep quality in preoperative anxiety-related insomnia. However, dexmedetomidine offers better sleep initiation and daytime functionality.
A randomized clinical trial sought to determine the efficacy and safety of intranasal dexmedetomidine (Dex) vs. oral lorazepam in patients experiencing anxiety-related sleep trouble before surgery. In total, 90 volunteers were randomized into 3 groups:
The interventions were administered the night before surgery. Sleep quality (primary outcome) was assessed using the Leeds Sleep Evaluation Questionnaire (LSEQ). Secondary outcomes included sleep monitoring, sleep satisfaction, vital sign changes within 2 hours post-intervention, and adverse reaction rates.
The sleep monitoring data highlighted a notable reduction in sleep onset latency for the Dex group when compared to lorazepam and placebo groups. Total sleep time and sleep efficiency for Dex users closely mirrored those in the lorazepam group and significantly outperformed those in the placebo group, as shown in Table 1.
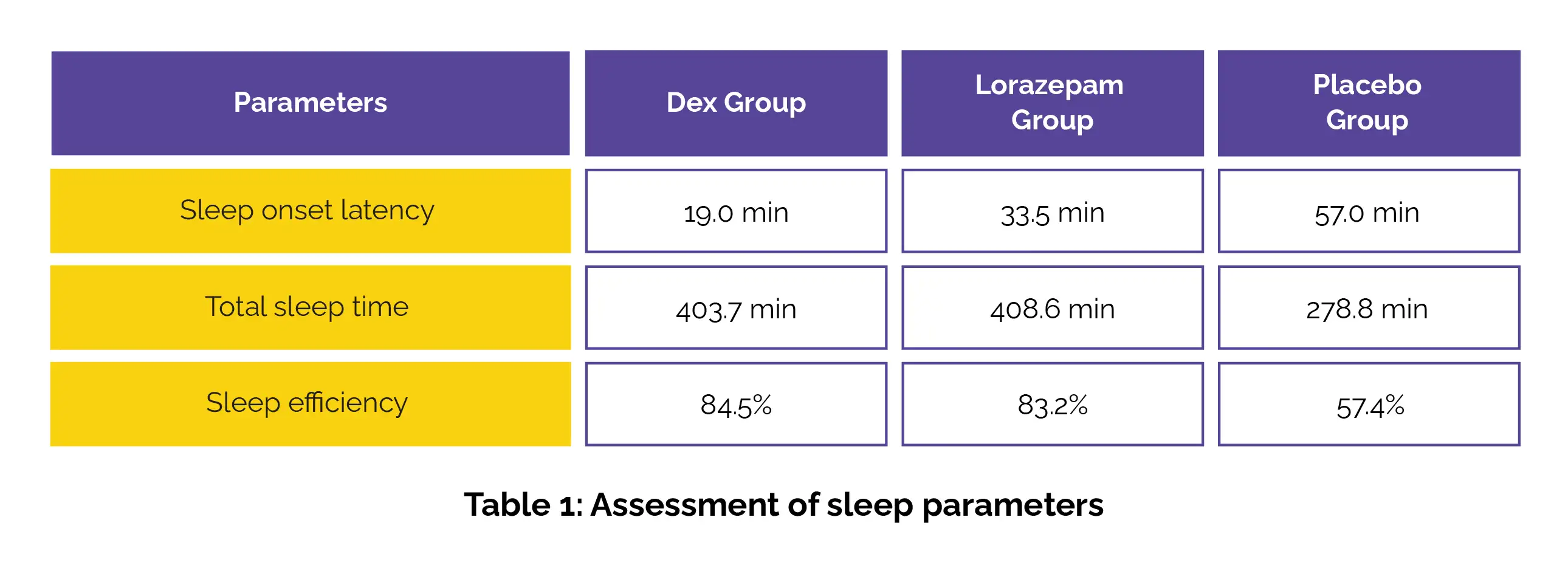
Additionally, the Dex group showed better improvements in ease of getting to sleep, ease of awakening from sleep, and improved alertness and behavior after waking when compared to the lorazepam group. Sleep satisfaction and overall sleep quality remained similar between Dex and lorazepam users. No serious adverse effects were witnessed in any group. These findings suggest that intranasal Dex could be a promising alternative for preoperative sleep management, particularly for those needing faster sleep induction and improved daytime functionality.
Drug Design, Development and Therapy
Intranasal Dexmedetomidine for the Management of Preoperative Anxiety-Related Insomnia: A Randomized, Three-Blinded, Clinical Trial Compared with Lorazepam and Placebo
Wen-yi Yang et al.
Comments (0)